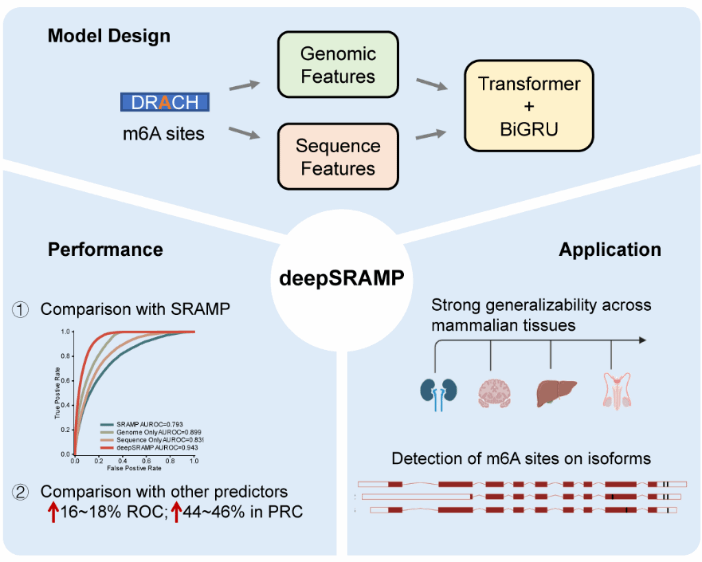
Recently, the research group led by Professor Cui Qinghua from the Wuhan Sports University (WHSU), in collaboration with Professor Wang Guoqing’s team from the College of Basic Medical Sciences at Jilin University, published a research article titled “A combined deep learning framework for mammalian m6A site prediction” in Cell Genomics. The study introduces a new deep learning algorithm, deepSRAMP, which integrates transformer neural networks and recurrent neural networks. Results showed that the performance of the deepSRAMP algorithm significantly improved over the machine learning-based SRAMP algorithm, with AUC and AUPRC increasing by 15.0% and 30.9%, respectively.

N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant RNA chemical modification known so far, playing significant molecular and biological roles in various physiological and pathological processes. Investigating the role of m6A in health and disease is a major scientific question, but this requires precise identification of m6A modification sites on RNA as a prerequisite.
Compared to recent algorithms incorporating sequence and genomic location features or deep learning models—such as WHISTLE and DeepPromise—deepSRAMP demonstrates superior performance (AUC: 0.966 vs. 0.805 and 0.783; AUPRC: 0.814 vs. 0.375 and 0.350). More importantly, deepSRAMP exhibits high accuracy in predicting m6A modification sites across different sequencing technologies, tissues or cell lines, and species. Additionally, deepSRAMP integrates a multi-instance learning approach, enabling m6A site prediction at the transcript isoform level, which provides a theoretical foundation for understanding the biological functions of m6A modifications. This research highlights the advantages of interdisciplinary integration across computational science and biomedicine, offering a high-performance AI tool for precise m6A site prediction.
Original Article: https://www.cell.com/cell-genomics/fulltext/S2666-979X(24)00326-4
The first authors of the paper are Fan Rui, a PhD graduate from the Department of Biomedical Informatics at the College of Basic Medical Sciences, Peking University (graduated in July 2024), and Cui Chunmei, a postdoctoral researcher at the same department (completed her postdoctoral work in November 2024). The corresponding authors are Dr. Cui Chunmei (Department of Biomedical Informatics, College of Basic Medical Sciences, Peking University), Professor Wang Guoqing (College of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University), Professor Cui Qinghua (School of Sports Medicine, Wuhan Sports University; School of Basic Medical Sciences, Peking University). The School of Sports Medicine at the Wuhan Sports University is the first affiliated institution of the paper. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62025102, 32301239, 81921001, and U23A20269).






